Memory Validator Tutorials

The Tutorials

How to detect memory leaks using Memory Validator

How to detect handle leaks using Memory Validator

How to detect memory leaks whilst your application is running

How to track memory allocations of a specific size using Memory Validator

How to monitor 3rd party memory allocation APIs using Memory Validator

How to view GDI objects using Memory Validator

How to detect COM Object Reference Count Errors using Memory Validator

Detecting memory leaks in a child process

Detecting memory leaks in a .Net Core application

Detecting memory leaks in a .Net Core application child process

Detecting memory leaks in a service

Detecting memory leaks in a service child process

Detecting memory leaks in an IIS ISAPI DLL

Detecting memory leaks in ASP.Net with IIS

Detecting memory leaks in ASP.Net with Web Development Server
Detecting memory leaks in a .Net Core application
This tutorial demonstrates launching a .Net Core application so that you can collect information about memory allocations and detect any memory leaks in the application.
Building the example application
For this tutorial we’re going to work with dotNetCoreLauncher which is located in <Memory Validator install directory>\examples\dotNetCore\dotNetCoreLauncher.
You will need to build this with Visual Studio 2019 (.Net Core 5) or Visual Studio 2022 (.Net Core 6). A solution file is provided for each version. If you’ve installed in the default program files location you’ll need to run Visual Studio in administrator mode to do the build.
We’re going to show you how to get detect memory leaks for Framework dependent .Net Core applications and also how to get detect memory leaks for self contained .Net Core applications .
Publishing the application
Publishing the .Net Core application allows you to create an application that is framework dependent, or which is self contained.
The following command will create a framework dependent version and a self contained x64 version using Visual Studio 2019 and Visual Studio 2022.
Open a command prompt with administrator privileges.
cd c:\Program Files (x86)\Software Verify\Memory Validator x64\examples\dotNetCore
publish.bat
You can also use publish_vs2019.bat and publish_vs2022.bat for use with specific versions of Visual Studio.
Framework dependent .Net Core
- Launch the sample application. Click on the launch icon on the toolbar.

- The Launch Application or Service dialog is displayed.
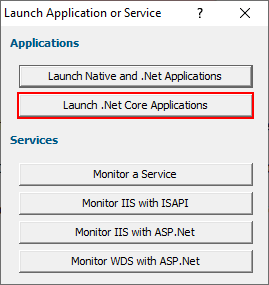
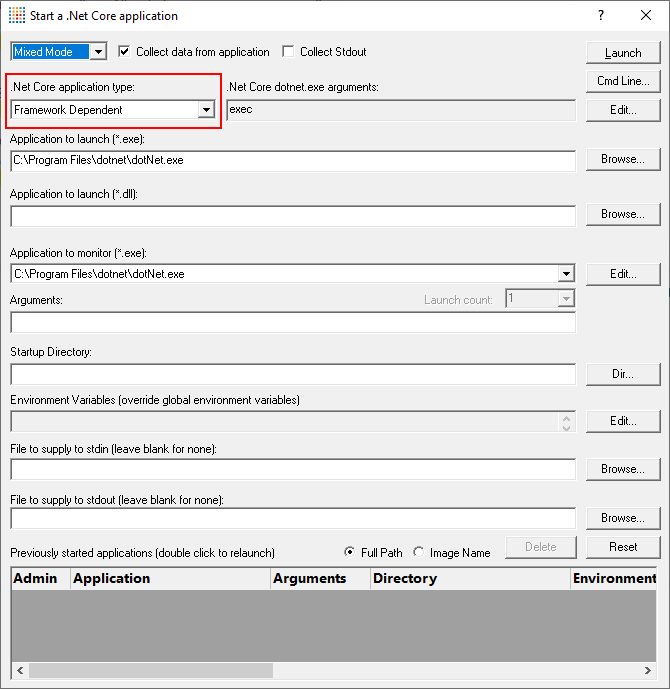
- Click Launch .Net Core Applications. The Launch .Net Core application dialog is displayed. By default it is configured for Framework Dependent .Net Core applications. You can change that from the .Net Core Application Type combo. For this tutorial we’ll leave it set to Framework Dependent.
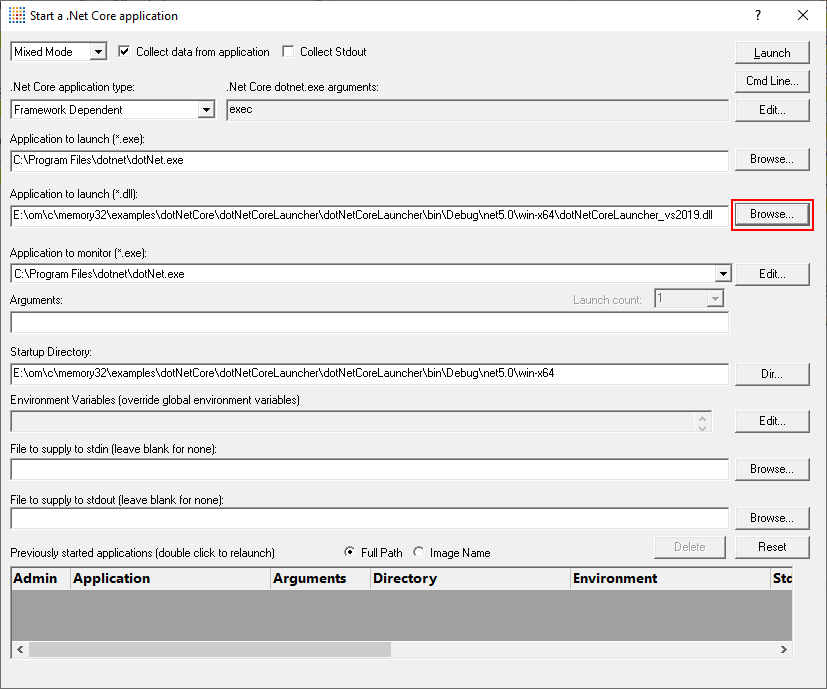
- Select the dotNetCoreLauncher_vs2019.dll using the Browse… button next to the Application to launch (*.dll) field. When you do this the Application to launch (*.exe) and Application to Monitor fields are populated with the .Net Core runtime, and the Application to launch (*.dll) is populated with the choice of dll.
- Click the Launch button to launch the application.
- The .Net Core dotNet.exe runtime is started to run the dotNetCoreLauncher_vs2019.dll application.
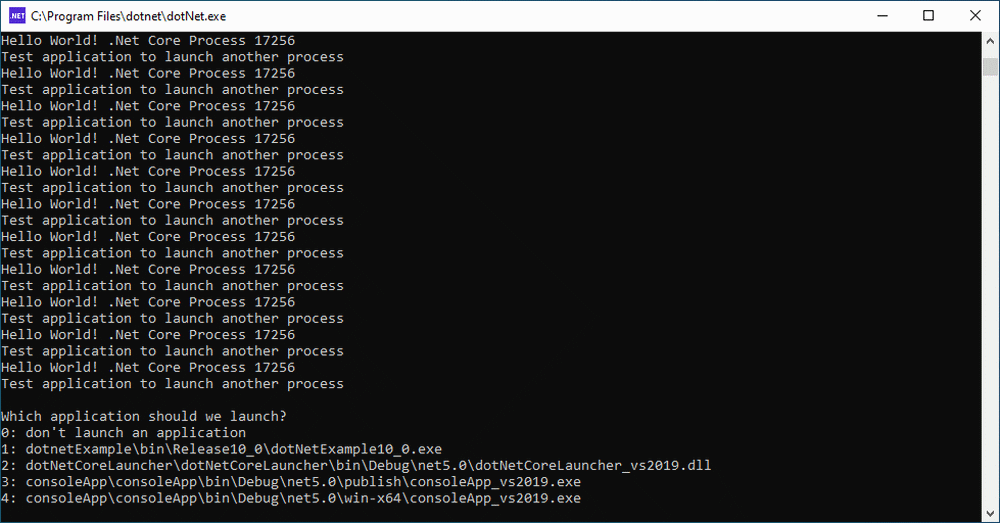
- Whilst Memory Validator is instrumenting the application various progress dialogs are displayed. The display of Memory Validator updates to show summary statistics for .Net and native memory.
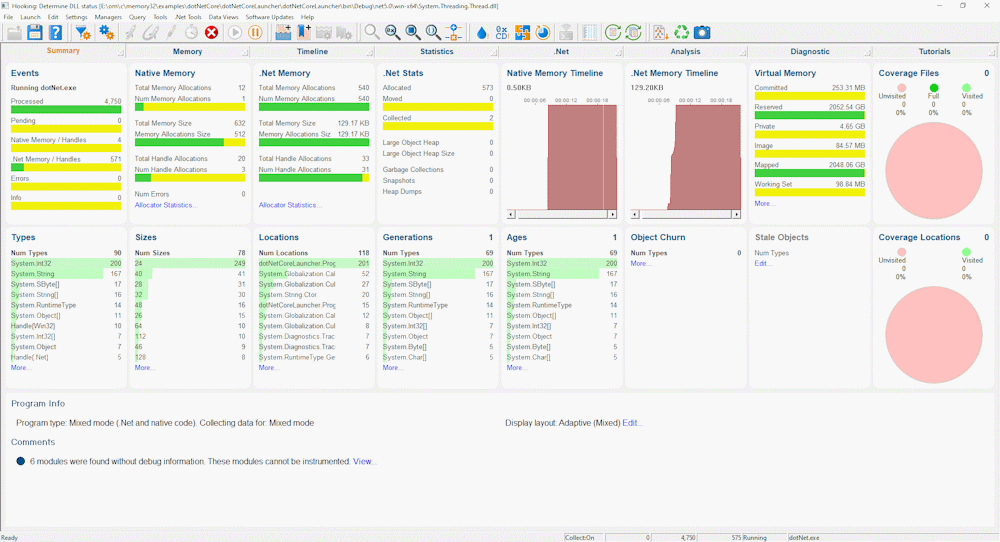
- Close dotNetLauncher by making a choice between 0 and 4. Any other choice repeats the menu. The application closes. Memory Validator processes any remaining data and displays the final results.
- The memory leak results are displayed on the Summary, Memory, Statistics, and Timeline tabs. Additional .Net specific analysis can be performed on the .Net tab. These have been discussed in previous tutorials, we will not repeat that discussion here.
Self Contained .Net Core
- Launch the sample application. Click on the launch icon on the toolbar.

- The Launch Application or Service dialog is displayed.

- Click Launch .Net Core Applications. The Launch .Net Core application dialog is displayed. Change the .Net Core application type to Self Contained using the .Net Core Application Type combo.
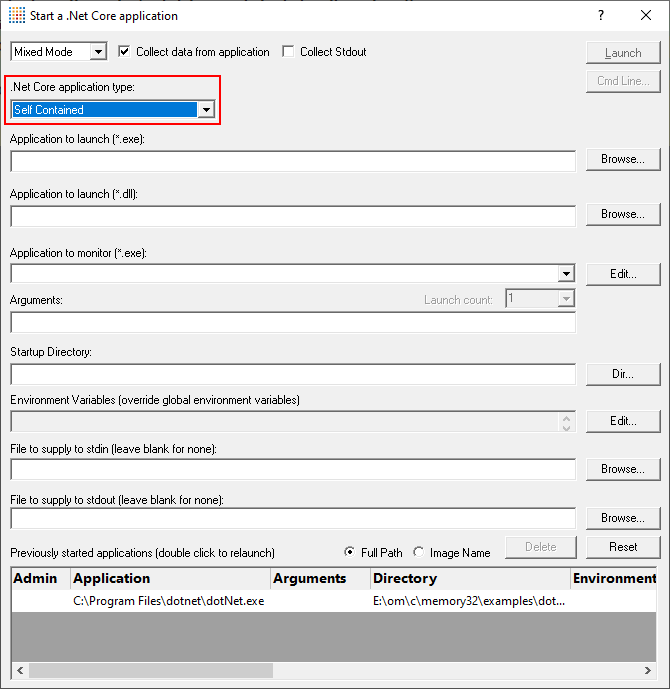
- Select the dotNetCoreLauncher_vs2019.exe using the Browse… button next to the Application to launch (*.exe) field. When you do this the Application to launch (*.dll) and Application to Monitor fields are populated with the executable, and the Application to launch (*.dll) is populated with a .Net Core dll that has the same name as the executable.
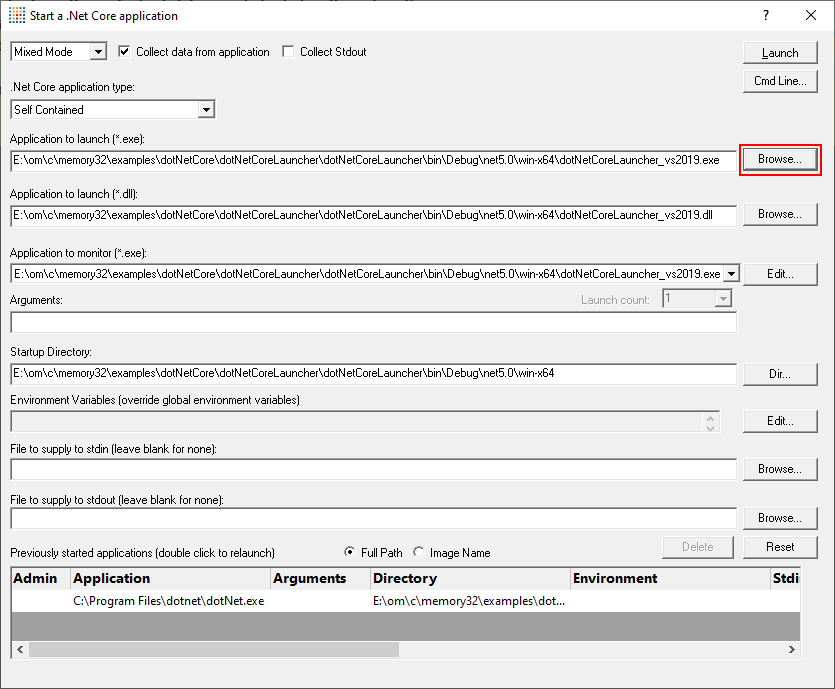
- Click the Launch button to launch the application.
- The .Net Core dotNetCoreLauncher_vs2019.exe runtime is started to run the dotNetCoreLauncher_vs2019.dll application.

- Whilst Memory Validator is instrumenting the application various progress dialogs are displayed. The display of Memory Validator updates to show summary statistics for .Net and native memory.
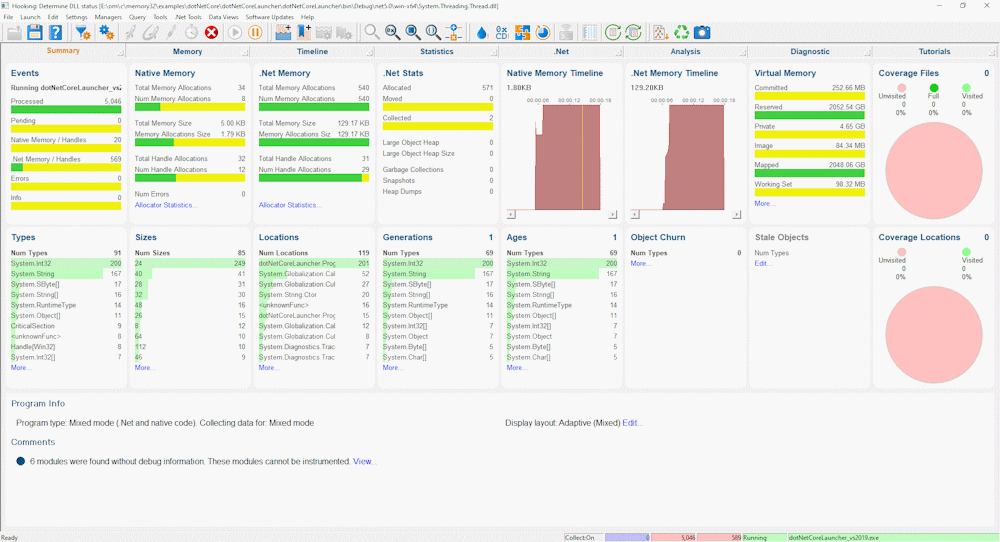
- Close dotNetLauncher by making a choice between 0 and 4. Any other choice repeats the menu. The application closes. Memory Validator processes any remaining data and displays the final results.
- The memory leaks results are displayed on the Summary, Memory, Statistics and Timeline tabs. Additional .Net specific analysis can be performed on the .Net tab. These have been discussed in previous tutorials, we will not repeat that discussion here.