The Collect tab allows you to specify which groups of hooks are installed in the target program when a session starts.
Changing the hooks that will be installed
Once installed, the group of installed hooks cannot be changed, so changing these settings is only effective on the next session with the target program.
The following image shows all the default options:
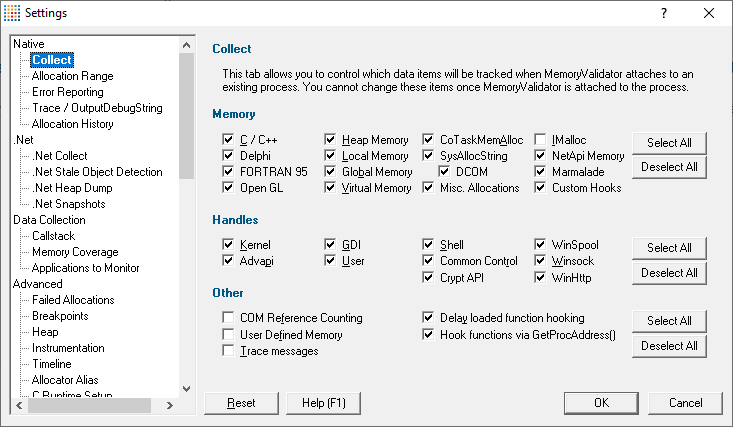
 Hooks specified here will be overridden by inclusion in the process modules list of the Hooked DLLs settings.
Hooks specified here will be overridden by inclusion in the process modules list of the Hooked DLLs settings.
Each of the Memory, Handles and Other checkboxes includes or excludes the relevant hooks for tracking the following items
Memory hooks
•C / C++  install hooks for C runtime heap
install hooks for C runtime heap
•Delphi  Delphi runtime heap
Delphi runtime heap
•Fortran 95  Fortran runtime heap
Fortran runtime heap
•Open GL  Open GL handles
Open GL handles
•Heap Memory  install hooks for HeapAlloc, HeapRealloc, HeapFree functions
install hooks for HeapAlloc, HeapRealloc, HeapFree functions
•Local Memory  LocalAlloc, LocalReAlloc, LocalFree functions
LocalAlloc, LocalReAlloc, LocalFree functions
•Global Memory  GlobalAlloc, GlobalReAlloc, GlobalFree functions
GlobalAlloc, GlobalReAlloc, GlobalFree functions
•Virtual Memory  VirtualAlloc, VirtualFree, VirtualAllocEx, VirtualFreeEx groups of allocation functions
VirtualAlloc, VirtualFree, VirtualAllocEx, VirtualFreeEx groups of allocation functions
•CoTaskMemAlloc  CoTaskMemAlloc group of allocation functions
CoTaskMemAlloc group of allocation functions
The preferred way of allocating memory in COM objects.
•SysAllocString  SysAllocString group of allocation functions
SysAllocString group of allocation functions
Allocates, reallocates and deallocates BSTR objects (OLE Strings).
•DCOM  an additional group of SysAllocString hooks are inserted for use in DCOM transactions
an additional group of SysAllocString hooks are inserted for use in DCOM transactions
Only available when SysAllocString is selected above, and not required for most applications.
•Misc. Allocations  miscellaneous allocation functions
miscellaneous allocation functions
•IMalloc  IMalloc functions
IMalloc functions
The old way of allocating memory in COM objects, prior to the introduction of CoTaskMemAlloc.
See also, notes about IMallocSpy below.
•NetApi Memory  NetApi allocation functions
NetApi allocation functions
•Marmalade  Marmalade game SDK allocation functions
Marmalade game SDK allocation functions
s3eMalloc, s3eRealloc, s3eFree, s3eBaseMalloc, s3eBaseRealloc, s3eBaseFree
•Custom Hooks  hooks for allocation functions tracking custom memory
hooks for allocation functions tracking custom memory
Default settings are with all memory hooks selected, except for IMalloc.
 Marmalade?
Marmalade?
For more information about working with Marmalade read Working with Marmalade game SDK.
 IMallocSpy?
IMallocSpy?
We do not recommend using the IMallocSpy option.
We have noticed that some functions (SysAllocString) cause many allocations to be reported by IMallocSpy, and yet the equivalent deallocation function SysFreeString does not cause the same allocations to be reported as deallocated by the IMallocSpy interface. This results in Memory Validator displaying misleading information. We recommend that the memory hooks for CoTaskMemAlloc, SysAllocString and Misc Allocations are used rather than IMallocSpy.
Handle hooks
•Kernel  install hooks for handles allocated in Kernel32.dll
install hooks for handles allocated in Kernel32.dll
•Advapi  handles allocated in Advapi32.dll
handles allocated in Advapi32.dll
•GDI  handles allocated in gdi32.dll
handles allocated in gdi32.dll
•User  handles allocated in user32.dll
handles allocated in user32.dll
•Shell  handles allocated in shell32.dll
handles allocated in shell32.dll
•Common Control  handles allocated in comctl32.dll
handles allocated in comctl32.dll
•Winspool  printer spool handles
printer spool handles
•Winsock  socket handles
socket handles
•WinHttp  http handles
http handles
Default settings are with all handle hooks selected.
Other hooks
•COM Reference Counting  install hooks for tracking COM object creation and reference count tracking.
install hooks for tracking COM object creation and reference count tracking.
See section below regarding possible erratic behaviour when using COM reference counting hooks.
•Trace Messages  tracking TRACE() messages and OutputDebugString()
tracking TRACE() messages and OutputDebugString()
•Delay loaded function hooking  functions which are delay loaded will be hooked as the functions are resolved by the delay loading process
functions which are delay loaded will be hooked as the functions are resolved by the delay loading process
Not all DLLs are delay loaded, but typical examples are COMCTL32.DLL and some COM libraries.
If this option is not selected then any functions that would normally be hooked, but which have been delay loaded, will end up not being hooked.
•Hook functions via GetProcAddress()  calls that are made to functions via a pointer obtained from GetProcAddress() will be hooked.
calls that are made to functions via a pointer obtained from GetProcAddress() will be hooked.
•User Defined Memory  calls to the Memory Validator API to track user defined calls will be allowed to send data to the user interface
calls to the Memory Validator API to track user defined calls will be allowed to send data to the user interface
Default settings are with only Delay loaded function hooking enabled.
 GetProcAddress() Hooking?
GetProcAddress() Hooking?
If a function that is looked up via GetProcAddress() is also a function that would normally be hooked via Import Address Tables, turning this option on will mean that that function will be hooked even if it is called via pointer returned from GetProcAddress(). This is typical source of unreported leaks in many memory leak detection tools, they don't detect calls via pointers from GetProcAddress().
 COM Reference Counting?
COM Reference Counting?
Selecting COM Reference Counting can cause erratic program behaviour if a hook gets inserted incorrectly.
This is because the COM hooks alter the machine code of the program and can get confused by the program structure. This is not typical of user written COM objects, but is typical of Microsoft® COM objects which appear to share entry and/or exit points between common functions.
Random crashes: If a program crashes randomly at start up, or seems to get stuck in an infinite loop (cpu at 99%) try disabling COM Reference Counting and check to see if the program behaves normally.
Reset All - Resets all global settings, not just those on the current page.
Reset - Resets the settings on the current page.
